Schema Checks
Validate proposed changes to your schema are safe
Certain changes to your graph's schema (such as removing a field or type) might break one of your application's clients. GraphOS schema checks help you identify breaking changes before you make them. They can also help you identify when a potentially dangerous change is, in fact, safe.
You can review the results of schema checks inside GraphOS Studio from your graph's Checks page, helping you make informed decisions about evolving your graph:
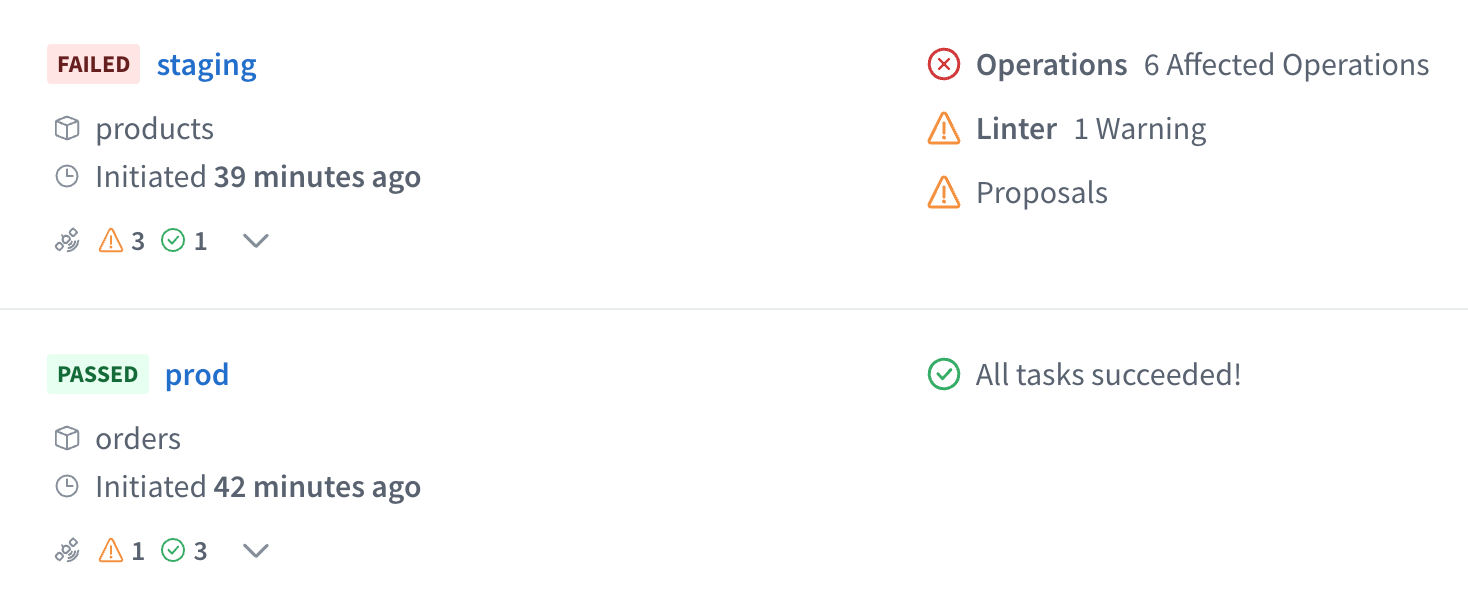
With the exception of contract checks, schema checks are free as part of all Apollo plans.
Types of checks
GraphOS can perform the following types of schema checks:
Composition checks: For supergraphs, verify whether your proposed changes to a subgraph schema successfully compose with your other subgraph schemas.
Operation checks: Compare your proposed schema changes against historical operations to verify whether the changes break any of your graph's active clients.
Linter checks: Analyze your proposed schema changes for violations of formatting rules and other GraphQL best practices.
Proposal checks (Enterprise only): Check whether your proposed schema changes have matching and approved schema proposals.
Contract checks (Enterprise only): When running schema checks on a source variant, also check whether your proposed schema changes break any downstream contract variants.
Most of this article covers composition and operation checks.
- For details on linter checks, see Schema linting.
- For details on proposal checks, see Schema proposals check configuration.
- For details on contract checks, see Contract checks.
Prerequisites
To enable schema checks for your supergraph, do the following if you haven't yet:
Make sure you've published all your subgraph schemas to GraphOS and that those schemas are up to date.
For operation checks, make sure your supergraph is sending operation metrics to GraphOS. GraphOS uses historical metrics to determine whether a potentially dangerous schema change is safe.
⚠️ CAUTION
If GraphOS has no operation metrics to compare against, all potentially dangerous schema changes result in a failed check.
- If you have a cloud supergraph, your router reports metrics automatically.
- See setup for other graph types.
Install the Rover CLI in your development environment and authenticate it with GraphOS.
Running your first check
Let's say you've made local changes to one of your subgraph schemas. After you complete the prerequisites, you can run schema checks against those changes with the rover subgraph check command.
ⓘ NOTE
If you have a monograph (which is not recommended), use rover graph commands instead of rover subgraph commands.
The rover subgraph check command looks like this:
rover subgraph check docs-example-graph@main --name products --schema ./schema.graphql
It requires the following:
Your registered graph's graph ref, which a string with the format
graph-id@variant-name(for example,docs-example-graph@main). This is available from your supergraph's README page in GraphOS Studio.The locally modified version of your schema. In the command above, the schema is provided via a
.graphqlfile.If your schema is not in a standalone
.graphqlfile, you can run your GraphQL server locally and pipe its schema directly fromrover graph introspect, like so:rover subgraph introspect http://localhost:4000 | rover subgraph check docs-example-graph@main --name products --schema -
Try changing something in the local version of your schema and see what happens! If everything is set up correctly, the command's output looks similar to the output shown in The check response.
The checks lifecycle
When you run rover subgraph check:
- GraphOS generates a diff between your local schema and the published schema for the variant you're checking against.
- GraphOS uses this diff to determine whether the changes affect any operations that have been executed against your supergraph within a customizable time window (by default, this is the last seven days).
- GraphOS returns the diff, along with a list of the operations affected by the changes.
- Rover prints the check result and returns a non-zero exit code if at least one breaking change is found.
The check response
Running rover subgraph check outputs the diff of all detected schema changes and highlights breaking changes:
$ rover subgraph check docs-example-graph@current --subgraph products --schema ./schema.graphqlValidated the proposed subgraph against metrics from docs-example-graph@currentCompared 1 schema changes against 24 operations┌────────┬────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ Change │ Code │ Description │├────────┼────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤│ PASS │ FIELD_CHANGED_TYPE │ field `Query.books`: type `[Book]` changed to `[Book!]` │└────────┴────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘View full details at https://studio.apollographql.com/service/docs-example-graph/checks/<DETAILS>
Each change to the schema is labeled either PASS or FAIL.
ⓘ NOTE
Because breaking changes are detected by analyzing recent operations, your graph must report metrics to GraphOS for schema checks to work. If there are no operation metrics to compare against, all potentially dangerous schema changes are labeled FAIL.
The rover subgraph check command returns a nonzero result if any check fails.
The output also includes a Studio URL that provides full details on the changes and their impact on existing clients and operations:
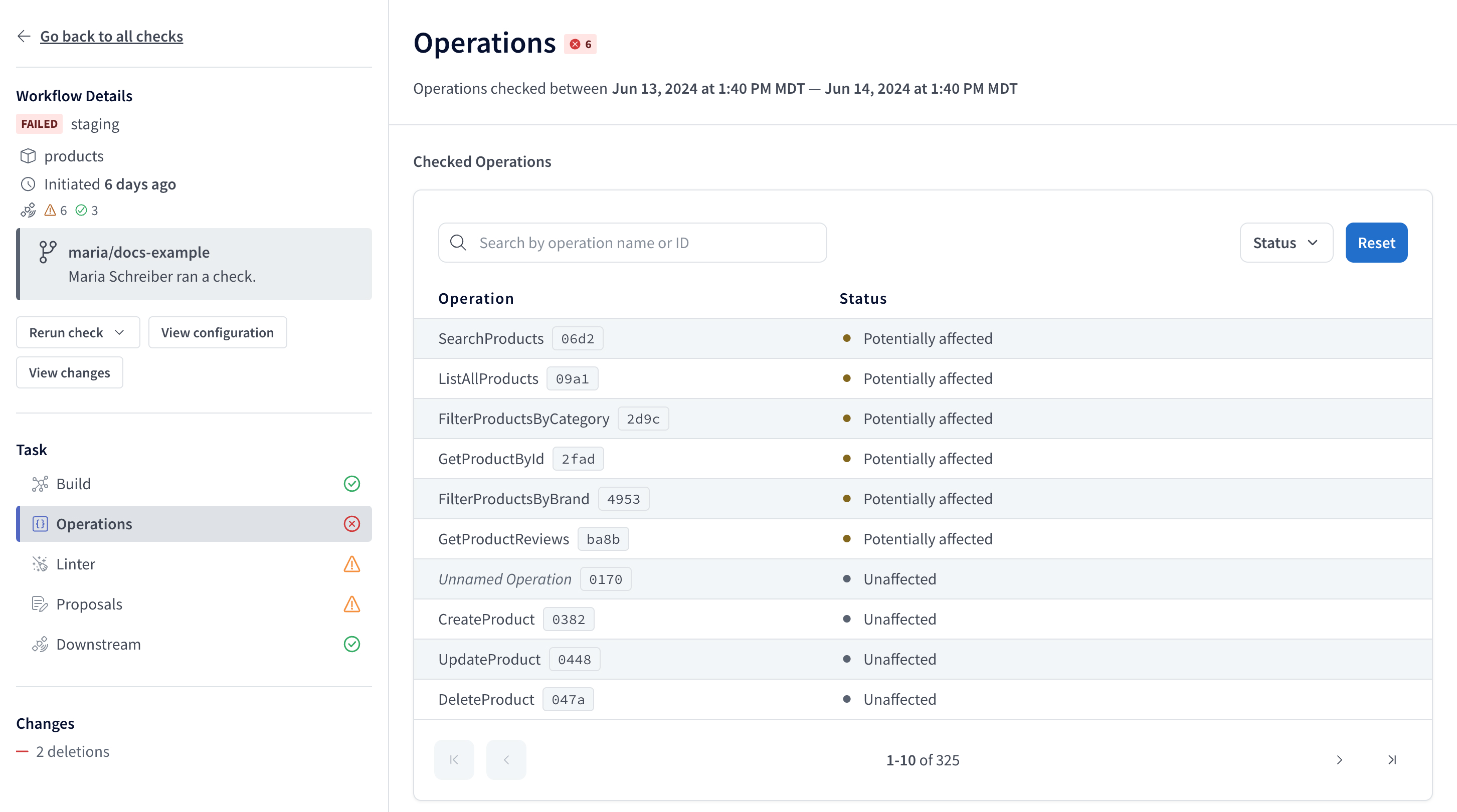
If you've integrated schema checks with your GitHub PRs, the Details link in your GitHub check takes you to this same details page.
If you run a check within a Git repository, rover subgraph check sends both the commit hash and that hash's author to GraphOS to display on the check. If you haven't integrated schema checks with GitHub, the author appears as Unknown. If you want to override author, commit, or other values, you can set environment variables in Rover to do so.
Rerunning checks
You can rerun checks from GraphOS Studio. Select the check and click Rerun check.
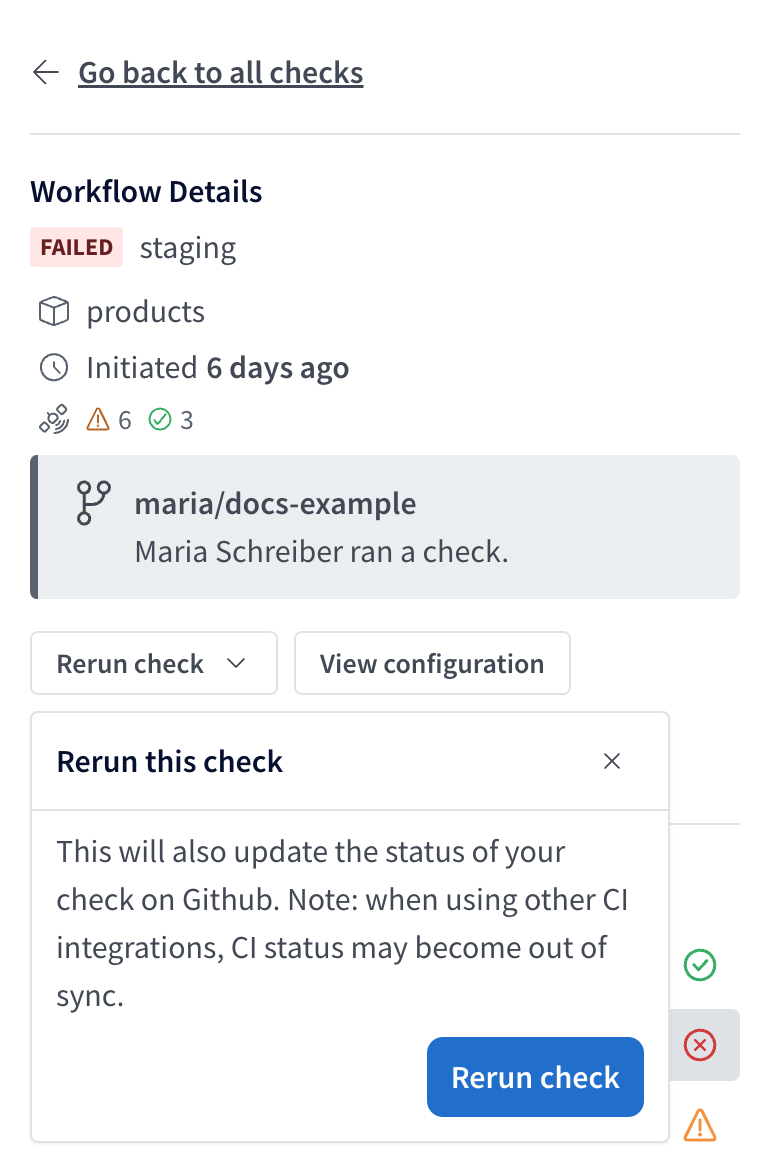
When you rerun a check, the new run uses the current check configuration options, regardless of the configuration at the time of the original run. Similarly, the new run's time window is based on the current time, not when the original check ran.
The new checks run incorporates any changes made to excluded or included clients, checked variants, and any operations marked as safe or ignored.
ⓘ NOTE
If you've integrated schema checks with your GitHub PRs, a rerun of the check also updates the status of the check in GitHub.
Composition checks
When you run rover subgraph check, GraphOS performs a composition check before performing any other checks. A composition check verifies that changes you make to a subgraph schema are valid GraphQL definitions and are compatible with your other subgraph schemas, enabling them to compose into a supergraph schema for your router.
If a composition check fails, Studio does not perform additional checks for the provided schema.
From your graph's Checks page in GraphOS Studio, you can click a particular composition check to view its result. If composition succeeded, you can view the composed supergraph schema. Regardless of success, you can view the proposed subgraph schema.
Operation checks
If a composition check succeeds, GraphOS then validates schema changes with operation checks. Operation checks use your graph's historical client operation data to determine whether any clients would be negatively affected by the proposed schema changes. For example, an operation check would flag a change that removes a field that multiple clients use in their operations.
Overriding flagged changes
Occasionally, schema checks might flag a change that you know is safe. For example, you might change an input type's field from nullable to non-nullable (usually a breaking change) when you're certain that your clients never provide a null value for the field.
You can override flagged changes on an operation-by-operation basis or update your check settings to ignore certain kinds of changes.
Override changes per operation
Org admins and Graph admins can override flagged changes on an operation-by-operation basis in GraphOS Studio. From the associated check's details page, select the Override dropdown under a flagged operation:
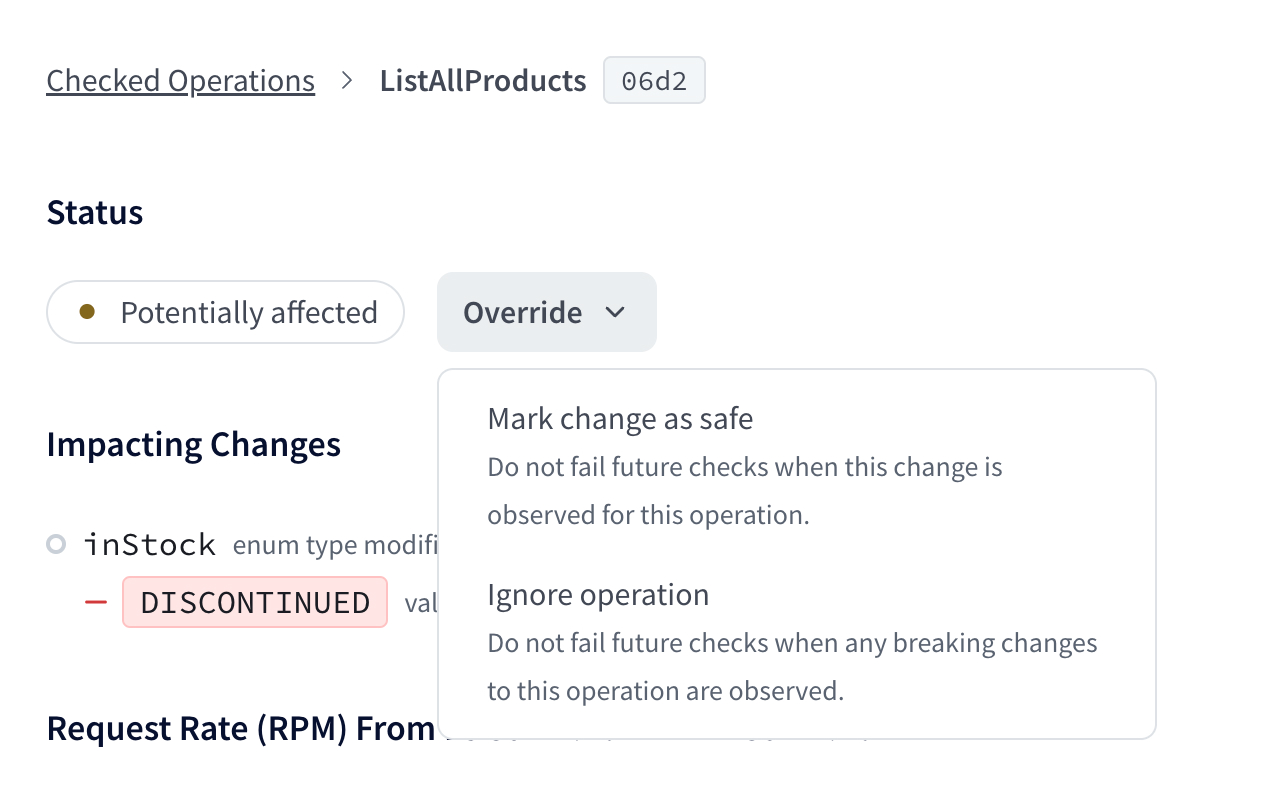
For each operation with flagged changes, you can override those changes in the following ways:
- Mark change as safe: In this case, schema checks will not flag these exact changes for the operation in any future execution. This effectively "approves" the changes for the operation.
- If a future check detects approved changes along with new unsafe changes to the operation, the new unsafe changes will be flagged.
- Ignore the operation: In this case, schema checks will completely ignore the operation when checking all changes in any future execution.
- This option is useful when you know an operation originates only from clients or client versions you don't actively support.
You can Undo an override from the banner that appears on any overridden operations.

Ignored conditions settings
You can update your check settings so operation checks don't flag the following kinds of changes:
Ignore breaking changes when there are no operations: Turning this setting on ignores any potentially breaking changes when an operation check is run against zero operations.
Ignore default value changes: Turning this setting on ignores any changes to default values.
ⓘ NOTE
This setting ignores default values changes but doesn't ignore default value removals.
You enable these settings from the Configuration tab of your variant's Checks page. Learn about other checks settings on the Configure Schema Checks page.
Linter checks
For more info on linter checks, see Schema linting.
Proposals checks
This feature is only available with a GraphOS Enterprise plan.
You can test it out by signing up for a free Enterprise trial.
For more info on proposals checks, see the schema proposals documentation.
Contract checks
This feature is only available with a GraphOS Enterprise plan.
You can test it out by signing up for a free Enterprise trial.
For more info on contract checks, see the contracts documentation.
Using in CI
Schema checks are especially useful when you add them to your CI pipeline (such as Jenkins or CircleCI). By doing so, you can obtain check results and display them directly on your team's pull requests.
We recommend defining a separate CI job for each variant of your schema (production, staging, etc.) that you want to validate your changes against. The rover subgraph check command returns a non-zero exit code when it detects a breaking change, meaning the job fails when the check fails.
Authenticating Rover
The rover config auth command is interactive, which means you shouldn't use it in CI environments. Instead, you can authenticate Rover with Studio by setting the APOLLO_KEY environment variable in CI. For details, see Configuring Rover.
Example configuration
The following config defines a schema check job for a CircleCI pipeline. Your config's syntax varies depending on your CI tool, but the job's steps are the same.
version: 2jobs:# ...other jobs...# Define a separate job for each environment you validate against.check_against_staging:docker:- image: circleci/node:12steps:- checkout- run: npm install# Start the GraphQL server. If a different command is used to# start the server, use it in place of `npm start` here.- run:name: Starting servercommand: npm startbackground: true# Make sure the server has enough time to start up before running# commands against it.- run: sleep 5# In CI environments, this command authenticates via the `APOLLO_KEY`# environment variable.- run: rover subgraph check docs-example-graph@current --name products --schema ./schema.graphql
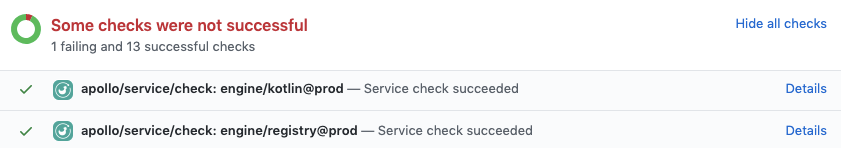
Integrating with GitHub
If you're using GitHub, you can install the Apollo Studio GitHub app. This app enables GraphOS to send a webhook back to your GitHub project on each call to rover subgraph check, providing built-in pass/fail status checks on your pull requests:
Integrating with other version control services
If you're using GitHub Enterprise, Bitbucket, or another version control service, we recommend setting up your CI tool to post a comment on each pull request with the results of schema checks. By surfacing schema diffs and breaking changes directly in your PR, you can avoid searching your CI logs to determine why a check failed.
Customizing checks
See Configuring schema checks.
Types of schema changes
Not every change to a schema is a potentially breaking change. Additive changes (such as adding a field to a type) are usually safe and do not affect active clients. Deletions and modifications (such as removing a field or changing a return type), however, can break clients that use affected types and fields.
Potentially breaking changes
Removals
These changes remove a schema element. If a removed element is actively being used by an operation, that operation will start returning an error.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
FIELD_REMOVED | A field used by at least one operation was removed. |
TYPE_REMOVED | A scalar or object used by at least one operation was removed. |
ARG_REMOVED | An argument used by at least one operation was removed from a field. |
TYPE_REMOVED_FROM_UNION | A type was removed from a union used by at least one operation. |
INPUT_FIELD_REMOVED | A field was removed from an input type. That field is referenced by an argument on another field that's used by at least one operation. |
VALUE_REMOVED_FROM_ENUM | A value was removed from an enum used by at least one operation. |
TYPE_REMOVED_FROM_INTERFACE | An object was removed from an interface used by at least one operation. |
Addition of required arguments
These changes add a required input to a schema element. If an operation is actively using an element of your graph and doesn't add the new required input argument, the graph will return an error to affected clients.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
REQUIRED_ARG_ADDED | A non-nullable argument was added to field that's used by at least one operation. |
NON_NULL_INPUT_FIELD_ADDED | A non-nullable field was added to an input object used by at least one operation. |
In-place updates
These changes update an existing schema element. If an operation is actively using an element that is updated, the operation might start receiving an error from your graph. It also might receive an unexpected result.
ⓘ NOTE
In some cases, in-place updates are compatible with affected clients at runtime (such as a type rename or a conversion from an object to an interface that uses the same fields). However, schema checks still marks these as breaking changes, because validation does not have enough information to ensure that they are safe.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
FIELD_CHANGED_TYPE | An existing field used by at least one operation changed its type. |
INPUT_FIELD_CHANGED_TYPE | An existing field of an input object changed its type. That field is referenced by an argument on another field that's used by at least one operation. |
TYPE_CHANGED_KIND | An existing type used by at least one operation changed its "kind." For example, an object type was changed to a union type. |
ARG_CHANGED_TYPE | An existing argument on a field used by at least one operation changed its type. |
Default arguments
These changes update the default value for an argument. If an operation is using an element of your graph and does not specify a value for this argument, the operation might get an unexpected result when the schema is updated if it was relying on the original default value.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
ARG_DEFAULT_VALUE_CHANGE | An existing field used by at least one operation had a default value added or changed. |
Non-breaking changes
These changes are detected by schema checks, but they are "safe." They never affect the behavior of any existing clients if deployed.
Schema additions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
FIELD_ADDED | A field was added to an existing type. |
TYPE_ADDED | A type was added to the schema. |
VALUE_ADDED_TO_ENUM | A value was added to an enum. If clients contain a switch statement on the enum's value and do not include a default case, this change might cause unexpected behavior. |
TYPE_ADDED_TO_UNION | A type was added to a union used by at least one operation. |
TYPE_ADDED_TO_INTERFACE | An interface was applied to an object used by at least one operation. |
OPTIONAL_ARG_ADDED | A nullable argument was added to an existing field. |
NULLABLE_FIELD_ADDED_TO_INPUT_OBJECT | A nullable field was added to an existing input object. |
Deprecations
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
FIELD_DEPRECATED | An existing field was deprecated. |
FIELD_DEPRECATION_REMOVED | A previously deprecated field is no longer deprecated. |
FIELD_DEPRECATED_REASON_CHANGE | The specified reason for a field's deprecation changed. |
ENUM_DEPRECATED | An existing enum was deprecated. |
ENUM_DEPRECATION_REMOVED | A previously deprecated enum is no longer deprecated. |
ENUM_DEPRECATED_REASON_CHANGE | The specified reason for an enum's deprecation changed. |
Descriptions
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
TYPE_DESCRIPTION_CHANGE | An existing type's description changed. |
FIELD_DESCRIPTION_CHANGE | An existing field's description changed. |
ENUM_VALUE_DESCRIPTION_CHANGE | An existing enum value's description changed. |
ARG_DESCRIPTION_CHANGE | An existing argument's description changed. |
Limits
Operation check cardinality
Operation checks will run against a maximum of 10,000 distinct operations. A warning message will display on the UI when a larger cardinality has been reached.
Input field usage reporting
GraphOS tracks operation usage. To deduplicate operations, Apollo uses operation signatures which denormalize the arguments and inputs. This means that the result of the operation signature does not track which fields on input types are used.
For example, GraphOS will not be able to track how many times the input field GetUsersInput.firstName is used in this schema:
type Query {getUsers(filters: GetUsersInput): [User]}input GetUsersInput {firstName: StringlastName: String}type User {id: ID!firstName: String!lastName: String!}